GUM THERAPY
Gum therapy is a vital component of modern dentistry, focused on preserving and improving the health of your gums. Healthy gums are the foundation for strong teeth and a radiant smile, making gum therapies a critical aspect of comprehensive oral care. From preventing and treating gum diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis to addressing cosmetic concerns such as gummy smiles, these therapies encompass a broad spectrum of treatments and procedures. Gum therapies often involve deep cleanings, gum grafting, laser therapy, and other advanced techniques, tailored to your unique oral health needs.
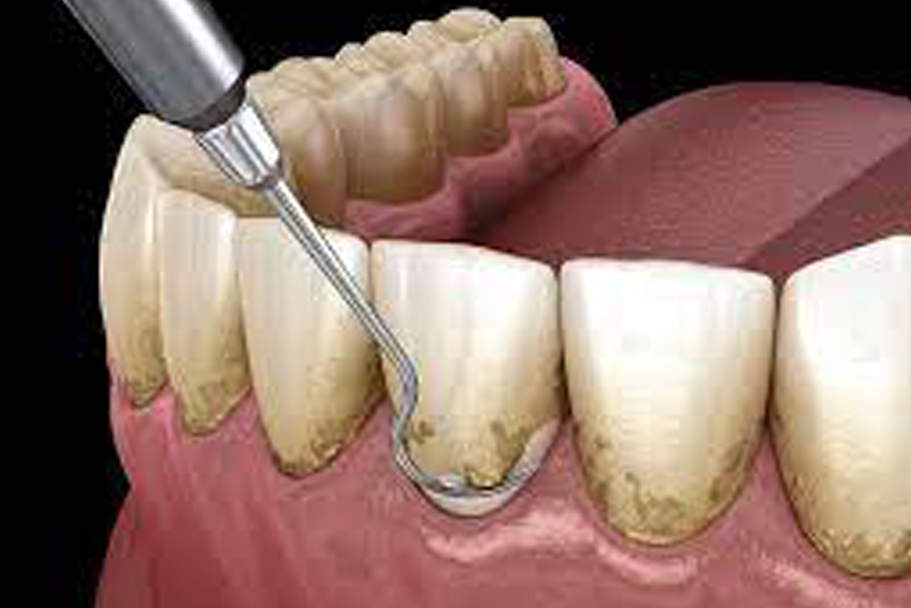
Gum therapy, also known as periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is a dental procedure aimed at treating gum disease by removing plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and below the gumline. It typically involves two main procedures: scaling and root planing. Here are the steps involved in gum therapy:
- Consultation and Evaluation:The process begins with an initial consultation with an orthodontist. They will examine your teeth, take X-rays, and possibly create molds of your teeth to create a personalized treatment plan.
- Local Anesthesia:To ensure patient comfort, a local anesthetic may be administered to numb the area being treated. This helps to alleviate any discomfort during the procedure.
- Scaling:Subgingival Scaling: The dentist or dental hygienist uses specialized tools to remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline. This process helps eliminate bacteria that contribute to gum disease.
- Root Planing:This involves smoothing out the rough surfaces of the tooth roots to prevent bacteria from reattaching. It also helps the gum tissue reattach to the tooth surface.
- Irrigation and Antimicrobial Agents:The treated area may be flushed with an antimicrobial solution to further reduce bacteria and aid in the healing process.
- Antibiotics (if necessary):In some cases, antibiotics or antimicrobial gels may be prescribed to address persistent infection or inflammation.
- Bite Adjustment (Occlusal Adjustment):In cases where the bite may be contributing to gum disease, adjustments may be made to ensure proper alignment of the teeth.
- Patient Education:The patient is educated on proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing techniques, flossing, and the use of antimicrobial mouthwashes. Diet and lifestyle changes may also be discussed.
- Periodontal Maintenance:For patients with chronic gum disease, ongoing periodontal maintenance appointments may be recommended. These cleanings are more extensive than regular cleanings and are scheduled more frequently.
- Home Care Routine:Patients are provided with personalized instructions on how to maintain optimal gum health at home, including recommended oral hygiene products.
- Monitoring Progress:Periodic evaluations are conducted to monitor the progress of gum therapy and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
It's crucial to note that gum therapy is typically performed by a dental hygienist or a periodontist (a specialist in gum diseases). The specific steps and techniques may vary depending on the severity of the gum disease and the individual patient's needs. Early intervention and consistent maintenance are essential for effectively managing gum disease and preventing its progression.
