JAW AND CHIN CORRECTION
Surgical correction of jaw and chin deformities, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a specialized procedure aimed at correcting structural abnormalities of the jaw and chin. These deformities can affect both function (such as chewing and speaking) and aesthetics.
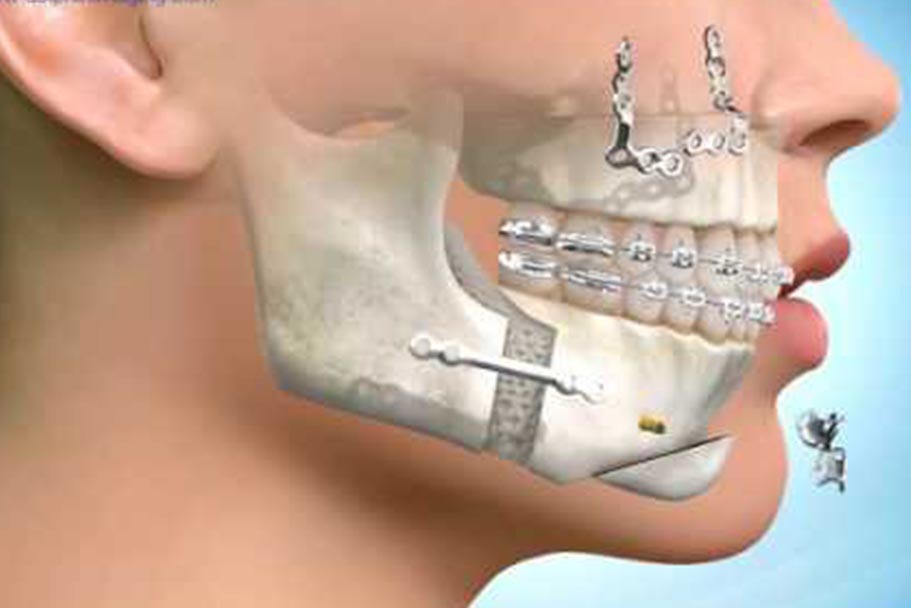
Here are the key aspects of surgical correction of jaw and chin deformities:
Common Types of Jaw and Chin Deformities:
- Underbite (Prognathism): The lower jaw protrudes forward, causing the lower teeth to extend in front of the upper teeth.
- Overbite (Overjet): The upper jaw protrudes forward, causing the upper teeth to overlap the lower teeth significantly.
- Open Bite: There is a gap between the upper and lower front teeth when the mouth is closed.
- Crossbite: The upper teeth fit inside the lower teeth, causing misalignment.
- Asymmetry: The jaw or chin is uneven, leading to facial asymmetry.
- Consultation and Evaluation: The process starts with a consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon or a craniofacial surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon evaluates the patient's condition, discusses their concerns, and explains the surgical process.
- Preoperative Planning: Advanced imaging techniques like 3D CT scans and digital models are used to plan the surgery in detail. This helps the surgical team determine the precise adjustments needed.
- Anesthesia: Orthognathic surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring that the patient is completely asleep and comfortable throughout the procedure.
- Incisions and Adjustments: The surgeon makes precise incisions inside the mouth to access the jawbones. Using specialized instruments, they make the necessary adjustments to reposition the jaw and chin bones.
- Fixation and Stabilization: In some cases, small plates, screws, or wires may be used to secure the bones in their new positions. These are often made of biocompatible materials that will remain in the body permanently.
- Closure of Incisions: The incisions are closed using dissolvable sutures. In some cases, the surgeon may choose to use external incisions, particularly for chin surgeries.
- Postoperative Care and Recovery: Patients are provided with specific instructions for postoperative care, including dietary restrictions, pain management, and follow-up appointments.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Orthognathic surgery often involves collaboration with orthodontists, who help align the teeth before and after surgery for optimal results.
- Functional and Aesthetic Improvement: Beyond aesthetics, orthognathic surgery aims to improve chewing, speech, and overall facial harmony.
- Recovery Time: The initial recovery period may take a few weeks, during which patients may experience some swelling and discomfort.
- Long-Lasting Results: Orthognathic surgery provides permanent improvements to jaw and chin alignment.
- Patient-Centered Care: Each surgery is tailored to the individual patient's needs, ensuring a personalized approach.
Procedure Overview:
Considerations and Important Points:
Orthognathic surgery is a complex procedure that requires expertise and precision. It can significantly improve both the functional and aesthetic aspects of the jaw and chin, leading to a better quality of life for individuals with these deformities. Consulting with a board-certified oral and maxillofacial surgeon or craniofacial surgeon is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation and treatment plan.
